
Starting a new job is exciting but can also be overwhelming – especially when faced with a contract full of legal jargon. However, understanding the types of employment contracts you’re signing is crucial.
It’s like having a roadmap to your job, outlining what’s expected of you and what you can expect in return. And let’s be real, nobody wants to stumble into a breach of contract accidentally!
In this article, I will break down the most common types of employment contracts – from permanent to freelance and everything in between. I will give you the lowdown on the pros and cons of each so you can feel confident and prepared for whatever your new job throws your way.
So, if that is what you need, this article is a must-read for you! Therefore, keep on reading this blog till the end to learn more…
Understanding Employment Contracts
An employment contract is like a promise between you and your employer. It’s a written agreement that outlines the terms and conditions of your job, including your rights and responsibilities.
Think of it like a roadmap to your employment journey. It shows you what’s expected of you, what you can expect from your employer, and what happens if things don’t go according to plan.
A typical employment contract includes details like:
- Your job title and responsibilities
- Your salary and benefits
- How many hours will you work, and when
- How much notice you’ll get if the job ends
- What happens if you want to leave or if your employer wants you to leave
Having a contract in place protects both you and your employer. It helps prevent misunderstandings and ensures everyone is on the same page.
But here’s the thing: contracts can be tricky to understand, especially if you’re new to the workforce. That’s why it’s essential to read yours carefully and ask questions if you’re unsure about anything.
Types of Employment Contracts
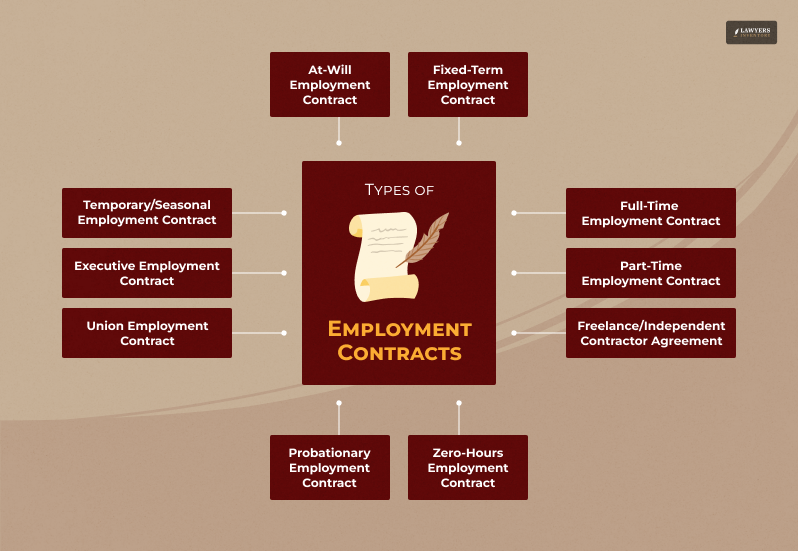
When it comes to understanding employment contracts, you must first know what type of employment contract you are getting. Some of the significant types of employment contracts that exist are:
- At-Will Employment Contract: No fixed term; employer or employee can terminate anytime.
- Fixed-Term Employment Contract: Specifies a start and end date, and the employer must provide notice or pay damages if terminated early.
- Full-Time Employment Contract: Standard 40-hour workweek, benefits, and job security.
- Part-Time Employment Contract: Fewer than 40 hours per week, often limited benefits.
- Freelance/Independent Contractor Agreement: Self-employed, project-based, no benefits.
- Temporary/Seasonal Employment Contract: Short-term, limited duration, often no benefits.
- Probationary Employment Contract: Trial period before becoming permanent.
- Union Employment Contract: Collective bargaining agreement between employer and union.
- Executive Employment Contract: High-level executives often include severance packages.
- Zero-Hours Employment Contract: No guaranteed hours, work as needed.
Let us now go through each of them in detail and understand their implications!
1. At-Will Employment Contract
An At-Will Employment Contract means you can be hired or fired anytime without reason or notice. It’s like an “as-needed” arrangement.
Your employer can terminate your job at their discretion, and you can also leave whenever you want. This type of employment contract offers flexibility but also uncertainty. Think of it like a “no-strings-attached” agreement.
You’re not locked into a specific term but don’t have guaranteed job security. It’s essential to understand that your employer can change the terms or end the contract without penalty or warning.
2. Fixed-Term Employment Contract
A Fixed-Term Employment Contract is like a promise with a deadline. You agree to work for a specific period, say 1-3 years and your employer promises to keep you until the end of that term. It’s like a commitment with a clear start and end date.
During this time, your employer can’t just let you go without a good reason or paying damages. You also can’t just quit without notice or penalty.
This type of contract offers stability and security but also limits flexibility. It is more or less like a “commitment with a clear expiration date.”
3. Full-Time Employment Contract
A Full-Time Employment Contract is like a long-term partnership. You agree to work a standard 40-hour week, and your employer commits to providing a steady income, benefits, and job security.
It’s like a mutual promise to work together for the foreseeable future. With a full-time contract, you can expect:
- A regular salary
- Benefits like health insurance and paid time off
- Job security and stability
- Opportunities for growth and advancement
This is like a “career home” where you can settle in, grow, and build a future with your employer.
4. Part-Time Employment Contract
A Part-Time Employment Contract is like a flexible friendship. You agree to work fewer hours than a full-time schedule, often less than 40 hours a week.
Your employer needs help, but not full-time, and you can balance work with other things in your life. Part-time contracts usually offer:
- Fewer hours and more flexibility
- Lower pay, but still a steady income
- Limited benefits, or none at all
- Less job security compared to full-time
Unlike full-time employment contracts, this one is a “casual collaboration” where you work together with your employer part-time, with more freedom to pursue other interests.
5. Freelance/Independent Contractor Agreement
As a freelancer or independent contractor, you’re essentially your own boss. You’re hired to do a specific job or project, and once it’s done, the agreement ends.
It’s like a project-based partnership, where you bring your expertise and collaborate with the client on a flexible, often remote basis.
This type of agreement means you’re paid for your specific work, not a steady salary. You’re also responsible for your benefits, taxes, and expenses – which can be a bit more complicated but also gives you more control over your finances.
The best part? You can work with multiple clients and choose projects that excite you. It’s like a series of “collaborative gigs” where you bring your skills to the table, work together on a project, and then move on to the next adventure!
6. Temporary/Seasonal Employment Contract
A Temporary/Seasonal Employment Contract is like a short-term helping hand. They hire you to lend a hand during a busy period or for a specific project. It’s a great way to gain experience, build your network, and make extra money.
This type of contract is usually for a limited time, like a summer internship or a holiday season job. When the busy period or project is over, your job ends, too.
Keep in mind that you might not get benefits or job security, but you’ll still get to be part of a team and make a difference. It’s like a “short-term teamwork” where you pitch in, help out, and then move on!
7. Probationary Employment Contract
A Probationary Employment Contract is like a “trial run” for a new job. It’s a temporary agreement that lets your employer test the waters to see if you’re a good fit for the role and the company. Think of it like a “getting to know you” period.
During this time (usually 3-6 months), your employer will closely monitor your performance, attendance, and overall fit with the team.
If everything goes well, the contract often converts to a permanent position. But if not, the employer can let you go without the usual notice period. It’s like a “test drive” before committing to a long-term partnership!
8. Union Employment Contract
Joining a union is like becoming part of a supportive team that’s got your back.
When you’re part of a union, you’re not alone in negotiating with your employer for better pay, benefits, and working conditions. The union represents you and your colleagues, ensuring everyone gets a fair deal.
Together, the union and employer agree on a contract covering important stuff like fair wages and benefits, safe working conditions, job security, and how to resolve disputes.
It’s like having a collective voice that says, “Hey, we deserve to be treated with respect and fairness!” And that’s a pretty powerful thing!
9. Executive Employment Contract
As a top leader in a company, you’re essentially a partner in the business. That’s why Executive Employment Contracts are designed to be high-level partnerships that outline your role, responsibilities, and rewards. Your company tailors these customized agreements to your unique situation and are meant to drive success.
They typically include perks like a competitive salary and bonus structure, stock options or equity, and top-notch benefits. But they also provide a clear path for growth and succession, so you know what’s expected of you and where you’re headed.
And, of course, they include termination clauses that protect your interests – just in case. It’s a commitment to excellence and a recognition of your value to the company.
10. Zero-Hours Employment Contract
Imagine being part of a team that’s always ready to jump in when needed. That’s what a Zero-Hours Employment Contract is like. You’re not tied to a fixed schedule or guaranteed a certain number of hours. Instead, you’re on call to work when the company needs you.
This flexible arrangement means that your employer only pays for your work hours. While that can be unpredictable, it also means you have the freedom to choose when you’re available.
Just keep in mind that this type of contract often doesn’t come with benefits or job security. It’s a casual, flexible setup that works for you and the company.
Know the Different Types of Employment Contracts
Your employment contract is a two-way street. It’s not just about what your employer expects from you but also about what you can expect from them.
Keep in mind that some contracts may overlap or have unique provisions, and laws vary by state. It’s essential to understand the specifics of your employment contract.
So, take the time to understand it, and don’t be afraid to speak up if you have any concerns!
Additional Reading:
- What Are the Elements of a Contract?
- All You Need To Know About Contract Repository
- All You Need To Know About Procurement Contracts
- What is Capacity in Contract Law? Legal Terms Simplified











0 Reply
No comments yet.