
What is an arbitration agreement? Well, though an agreement, it can sometimes be in the form of a clause.
Now, very simply put, it is an agreement or broader contract. Through it, parties can settle matters out of court. Therefore, it provides clear guidelines about the whole procedure to all parties.
All parties to the arbitration set the terms in an arbitration agreement after careful consideration. Here, they state their free and clear will to agree to settle a dispute out of court.
So, hold tight as we discuss all about arbitration agreements with a special light on the US system.
What Is Arbitration?
Arbitration is a way to settle disputes. It is one of the most important parts of alternate dispute resolution. Most importantly, it involves parties not taking the help of regular courts for dispute resolution.
Instead, they take the help of arbitrators. Moreover, the official arbitral tribunal also steps in to declare the decision. Thus, both parties try to get an arbitration award (final decision) that is in their favor.
This decision or award is binding in nature. So, it has the legal force of a court judgment unless the parties later go against it.
However, usually when parties choose arbitration as their method a dispute resolution, their options are limited. Later, they have fewer chances to choose litigation or review. Additionally, you may even have limited options for appeal compared to regular court cases. It’s not the same as court cases, other types of dispute resolution like mediation, or expert decisions.
Why Go For Arbitration And Not Litigation?
Well, some may find that going to court and filing a lawsuit, is the best way for dispute resolution. In a lawsuit, they have lawyers who are experts in dispute resolution. Moreover, they can even hire contract or regulatory lawyers whenever they wish.
However, people find arbitration agreements more suited to resolve disputes regarding consumer or employment contracts. They may not be the best case for white-collar crimes like embezzlement, but they have their use.
Arbitration has many advantages that litigation simply does not. For example, they are faster and more cost-effective to begin with. The agreement, although a long one, has fewer formalities than a whole litigation.
Additionally, arbitration is more of a party or dispute-centric approach. We usually do not find contract laws to be too “personalized”.
Thus, an arbitration allows parties to get special treatment. Moreover, they have more control over the dispute-resolution process. Additionally, when choosing arbitration over litigation, you will have an arbitrator to help you out on your specific subject matter.
Arbitration vs. Litigation: Which One Should You Choose?
When resolving disputes, choosing between arbitration and litigation can feel overwhelming. Both options have pros and cons, and the choice often depends on your unique situation. Let’s break it down to help you decide.
Arbitration is a private process where one or more arbitrators resolve disputes outside of court. It’s generally faster, less formal, and more flexible than litigation.
On the other hand, litigation involves resolving disputes in court, where a judge (and sometimes a jury) makes the final decision. It’s a formal process governed by strict legal procedures.
But which one should you choose? TBH, it is best to choose arbitration if you value privacy, speed, and flexibility. However, you can opt for litigation if your dispute requires strict legal procedures, public accountability, or appeals.
Ultimately, you must weigh your priorities carefully to make the best choice.
Here are some of the key differences to consider when choosing between Arbitration vs. Litigation:
1. Cost
Arbitration is usually less expensive than litigation because it avoids prolonged court procedures. However, the costs can rise if multiple arbitrators or institutions are involved. While costly due to court fees and legal representation, litigation might still be a better option for low-value disputes.
2. Time
Arbitration is quicker, with flexible schedules and limited procedural delays. In contrast, litigation can drag on for years, especially in backlogged court systems.
3. Confidentiality
Arbitration is private, making it ideal to keep disputes and outcomes confidential. Litigation, on the other hand, is a public process, and court records are usually accessible to the public.
4. Enforceability
Arbitration awards are enforceable in many countries under international treaties like the New York Convention, making it a strong choice for cross-border disputes. Litigation judgments may face more challenges in international enforcement.
5. Control Over the Process
Arbitration offers more control, allowing parties to choose arbitrators, venues, and rules. Litigation leaves these decisions to the courts.
Types of Arbitration Agreements and Their Content
What is an arbitration agreement for employment? What are the common contents of a business arbitration agreement? Let me tell you.
You can create arbitration agreements for various purposes. For example, it may be for business, employment disputes, etc.
When it comes to arbitration agreements, understanding the different types can help you make better decisions about resolving disputes.
Broadly, arbitration agreements fall into two categories: ad hoc arbitration agreements and institutional arbitration agreements. Let’s break these down in simple terms:
1. Ad Hoc Arbitration Agreements
In ad hoc arbitration, the parties involved organize the process themselves without relying on an institution.
This agreement offers flexibility because you and the other party have full control over the process, such as selecting arbitrators, rules, and procedures.
It’s often less expensive since there are no administrative fees for institutions. However, this flexibility can sometimes lead to delays if both sides can’t agree on procedural details.
Ad hoc arbitration works well if both parties are cooperative and knowledgeable about arbitration procedures.
It’s commonly used in domestic disputes where the legal framework is straightforward and doesn’t require extensive external oversight.
2. Institutional Arbitration Agreements
On the other hand, institutional arbitration involves a third-party organization, like the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) or the American Arbitration Association (AAA), to manage the process.
These institutions provide pre-established rules and a structured framework, making the process smoother and more predictable.
Although institutional arbitration is often more expensive due to administrative costs, it ensures that disputes are handled professionally and efficiently.
This type is ideal for complex or international disputes where the parties want a trusted body to oversee the arbitration.
Which Arbitration Type Should You Choose?
Choosing which arbitration type to choose—ad hoc or institutional arbitration—depends on several factors.
Understanding these considerations can help you select the option that best suits your situation.
Here are some of the factors to consider when you are choosing the arbitration agreement type:
1. Nature of the Dispute
For straightforward, domestic disputes, ad hoc arbitration may work well. It’s flexible and cost-effective.
However, if the dispute is complex or involves international parties, institutional arbitration provides a structured framework and professional oversight that ensures consistency and fairness.
2. Budget
Cost is a key factor. Ad hoc arbitration is usually less expensive since it avoids institutional fees.
But remember that unexpected delays or disagreements during the process could lead to additional costs.
Institutional arbitration, while pricier, often saves time and reduces procedural hiccups, making it worth the investment for high-stakes disputes.
3. Level of Expertise Needed
Institutional arbitration may be the better choice if the dispute involves technical or industry-specific issues. Institutions have access to a panel of qualified arbitrators and established rules, making the process more reliable.
4. Relationship Between Parties
If the parties are cooperative and willing to negotiate details, ad hoc arbitration might be sufficient. But when tensions run high, having an institution to mediate can prevent further conflict.
Arbitration Agreement: What are the Essential Components?
An arbitration agreement is a key document that lays the foundation for resolving disputes outside of court.
The agreement must be carefully crafted with essential components to ensure it serves its purpose effectively.
By including these elements, an arbitration agreement becomes a robust tool for resolving disputes efficiently and fairly.
Here’s a closer look at what these agreements typically include:
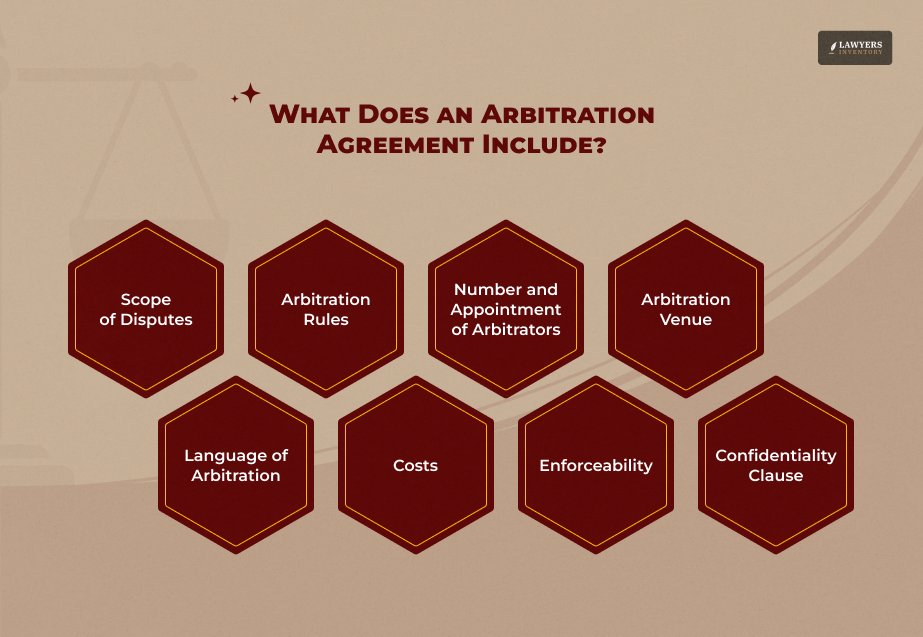
1. Scope of Disputes: This section defines the disputes covered under the agreement. For example, it may specify whether it applies to contractual issues, employment matters, or other conflicts. Being clear about the scope prevents confusion later.
2. Arbitration Rules: The agreement should outline which rules govern the arbitration process. If you’re using institutional arbitration, it might refer to the rules of bodies like the ICC or AAA. In ad hoc arbitration, the rules are usually customized by the parties.
3. Number and Appointment of Arbitrators: It’s important to state how many arbitrators will oversee the dispute—usually one or three—and how they’ll be chosen. This ensures fairness and prevents disputes over the selection process.
4. Arbitration Venue: The agreement must specify where arbitration will occur. This is particularly important in international disputes where the laws of the venue can affect the proceedings.
5. Language of Arbitration: For clarity, especially in global disputes, the agreement should state the language used during arbitration.
6. Costs and Fees: How arbitration costs and fees will be shared between the parties should be included.
7. Binding Nature and Enforceability: The agreement must explicitly state that the arbitrator’s decision will be final and binding, ensuring that both parties honor the outcome.
8. Confidentiality Clause: Since arbitration is private, a confidentiality clause ensures the proceedings and outcomes remain undisclosed.
Steps To Getting To An Arbitration Agreement
So, these are the necessary elements to reach arbitration agreements.
Agreement To Choose Arbitration
Both parties agree to choose arbitration- this is the common ground. Thus, this should be the accepted method of settlement of any potential disputes. The parties state their mutual will to arbitrate through a contract or an agreement.
Discussion On Agenda
Next, there is a discussion about what the arbitration will be about. It is important to know the issues or the exact type of disputes. Thus, only after knowing the problem will the parties know what to solve through arbitration.
Parties Get A Say On The Arbitrator
Yes, the parties can choose which arbitrators will help them. They can choose specific individuals.
Additionally, they can visit an arbitration agency and choose from their panel of established arbitrators. Moreover, they can also take the help of other selection methods.
Are There Specific Commercial Arbitration Rules For This Agreement?
Indeed, there are rules. They govern the arbitration through each stage. These rules also let the parties decide the physical and virtual location of the arbitration.
However, do these agreements guarantee confidentiality?
Yes. An arbitration agreement does contain a confidentiality clause. This clause safeguards the parties’ confidentiality and the dispute’s details.
Thus, complete access to confidentiality without making it to public records is possible through an arbitration agreement.
Why Would You Read Carefully Before Signing An Arbitration Agreement?
Employers do tend to include arbitration agreements in employment contracts. These agreements stand to their advantage.
Employees may sign them without grasping the terms, which may lead to heavy outcomes in the future.
Therefore, before you sign any contracts, it’s a good idea for you to hire a lawyer. For starters, the contract may seem confusing. Thus, asking a lawyer to explain the important parts is smart.
But can an employee still go to court despite an arbitration agreement?
Just because someone signed an arbitration agreement does not mean that the court is out of reach when they need it. They can still complain to the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission. The commission can sue the employer.
To Conclude
Thus, we now come to the end of our article on an arbitration agreement. Let us go through a short recap.
Arbitration agreements are like a plan set before a problem comes up. They are the deals between two parties, like employers and employees.
Moreover, these mostly dictate how to handle disagreements. These agreements decide that if there’s a conflict, later on, both sides will use a specific process to solve it.
It’s a way to work things out without going to court.
Read Also:
- What To Expect During Legal Consultation
- Everything You Need To Know About Super Lawyers
- Everything You Need To Know About Labor Law Attorneys











0 Reply
No comments yet.