
As an employee, you have more rights than you think! While you may know fundamental rights like fair pay and safe working conditions, many other rights can impact your job, career, and overall well-being.
From protection against workplace bullying to the right to take breaks and time off, numerous employee rights often fly under the radar.
It’s easy to overlook these crucial rights in today’s fast-paced work environment, but doing so can lead to burnout, stress, and even legal issues. Besides, you never know when you might need to check with your employment law attorney!
In this article, I will shine a light on the employee rights you didn’t know about but must learn to protect yourself, your job, and your future. Additionally, I will talk about the history and the need for these rights so that you can take control of your work life!
So, keep on reading this blog till the end to learn more…
Introduction to Employee Rights
The legal safeguards and perks employees are entitled to at work are called employee rights. These rights guarantee equitable, secure, and dignified treatment of employees.
Equal opportunity, a safe working environment, and just compensation are all examples of employee rights. Workers are entitled to benefits, compensation for their labor, and a work environment free from harassment and discrimination.
In addition, they are free to engage in collective bargaining, become union members, and report misconduct without fear of reprisal. One of the rights of employees is the ability to take time off, which includes holidays, sick days, and vacation time.
Furthermore, workers are shielded from unjust labor practices, including wrongful termination, and have the right to report infractions and pursue remedies.
The purpose of employee rights is to create a reasonable and fair workplace by balancing the power between employers and employees. Employees may safeguard a positive work-life balance and protect themselves against exploitation by being aware of and using their rights.
The History of Labor Laws
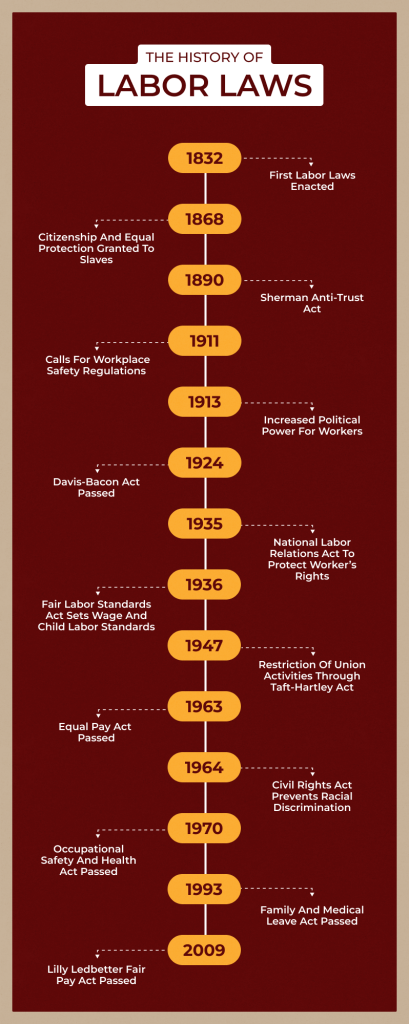
It is impossible to talk about employee rights without bringing labor laws into the picture. The leaders and the governing bodies had created these laws because workers wanted better working conditions, the right to organize, and fair treatment.
On the other hand, employers wanted to keep costs low and control workers. As a result, the leaders of countries across the world formed the International Labour Organisation (ILO) after World War I to address labor issues.
They created the ILO as part of the League of Nations to promote peace and cooperation. The ILO aimed to improve working conditions, protect workers, and promote social justice.
After World War I, many countries focused on rebuilding and protecting workers’ rights. The British Labour Party proposed a reconstruction program, and the American Federation of Labor (AFL) suggested incremental improvements through collective bargaining.
Two competing visions emerged for the post-war world. The International Federation of Trade Unions (IFTU) wanted to establish socialism and end wage labor. At the same time, the AFL preferred a more gradual approach.
The ILO’s first conference in 1919 adopted six conventions dealing with working hours, unemployment, and minimum age requirements. The ILO became part of the United Nations system in 1946.
Labor laws are a result of the struggle between workers and employers. The ILO plays a crucial role in promoting fair labor practices globally. Its formation and early conferences laid the groundwork for international labor standards.
Employee Rights and Indian Labor Laws
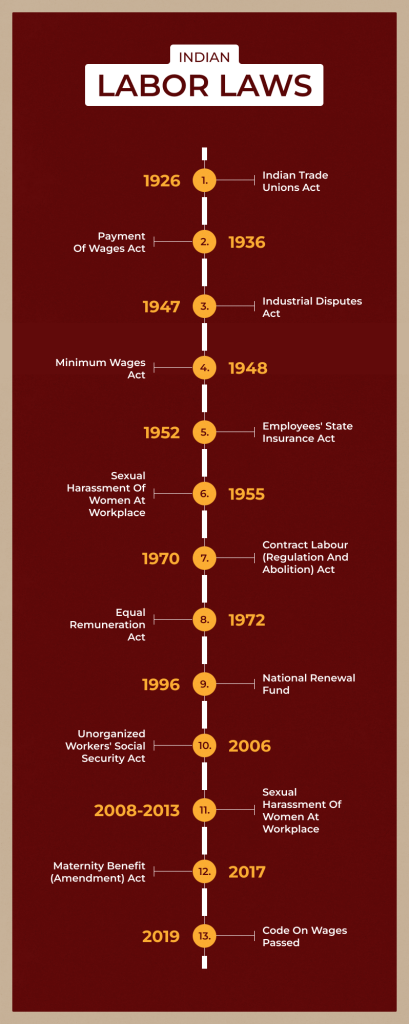
In India, various labor laws protect employee rights. These laws promote fair labor practices and ensure a safe working environment.
The Indian government has enacted several laws to safeguard the interests of employees and regulate employer-employee relationships.
Some of the key labor laws in India include the:
- Industrial Disputes Act of 1947, which provides for the resolution of disputes between employers and employees
- Factories Act of 1948, which regulates working conditions in factories
- Minimum Wages Act of 1948 ensures that employees receive fair compensation for their work.
The Employees’ Provident Funds and Miscellaneous Provisions Act of 1952 also provides employees with retirement benefits and social security.
Rights of Employees
Employees in India are entitled to fair wages, equal compensation for equal work, and a safe workplace. In addition, they are eligible for leave, gratuities, and provident funds.
To bargain for improved pay and benefits, workers can organize into trade unions and participate in collective bargaining.
The law also shields employees from unfair work practices like harassment, discrimination, and wrongful termination.
Enforcement of Labor Laws
The federal and state governments’ labor departments are in charge of enforcing labor regulations in India. Workers who believe someone has infringed upon their rights can file complaints with these departments.
Additionally, the government establishes labor courts and tribunals to settle disputes and give workers remedies.
In general, the goal of Indian labor laws is to provide a just and fair workplace; yet, for employees to properly use their rights, they must be aware of them.
Indian Labor Laws and Employee Rights Across Sectors

Workers in a variety of industries, such as manufacturing, construction, agriculture, and services, are protected by Indian labor laws.
These laws aim to guarantee safe working conditions, advance equitable labor practices, and offer social security benefits. Benefits such as minimum wages, overtime compensation, paid time off, and provident funds are guaranteed to employees.
Additionally, they are shielded from discrimination and other unfair labor practices like wrongful termination.
Common rights for all workers include fair compensation, equal compensation for equal work, and a secure workplace.
To bargain for improved pay and benefits, they can organize trade unions and participate in collective bargaining.
Furthermore, the government utilizes labor departments to enforce labor laws, and labor courts and tribunals are available to resolve disputes. If an employee’s rights are being violated, they can file a complaint.
The goal of Indian labor laws is to create a just and fair workplace. However, for employees to effectively exercise these rights, they must be aware of them.
Employee Rights in the Public Sector
Employee rights in the public sector in India and other parts of the world ensure fair treatment and protection for government employees. These rights include:
- Job security and protection from unfair dismissal
- Fair compensation and benefits, such as pensions and health insurance
- Safe working conditions and a healthy work environment
- Freedom from discrimination and harassment
- Right to collective bargaining and trade union membership
- Access to grievance procedures and dispute resolution mechanisms
In India, public sector employees are protected by laws such as the Central Civil Services (Conduct) Rules and the Industrial Disputes Act.
International organizations like the International Labour Organization (ILO) globally set public sector employee rights standards.
Public sector employee rights are essential to ensure government employees can work efficiently and effectively without fear of unfair treatment.
These rights also promote transparency, accountability, and good governance in the public sector.
By protecting employee rights, governments can attract and retain talented employees, improve public services, and build trust with citizens.
Employee Rights in the Private Sector
Employee rights in the private sector in India and other parts of the world protect employees from unfair treatment and ensure fair labor practices. These rights include:
- Right to fair wages and benefits
- Safe working conditions and a healthy work environment
- Protection from discrimination, harassment, and bullying
- Right to form and join trade unions and bargain collectively
- Protection from unfair dismissal and termination
- Access to grievance procedures and dispute resolution mechanisms
Laws like the Industrial Disputes Act, the Factories Act, and the Shops and Establishments Act protect workers in the private sector in India.
Organizations such as the International Labour Organization (ILO) establish global standards for employee rights in the private sector.
Protecting private sector workers’ rights is essential to ensuring they receive just treatment and respect. These privileges raise productivity, boost morale among staff members, and foster a positive workplace culture.
Private businesses can draw and keep top talent, build their brand, and promote social justice by upholding employee rights.
Employee Rights for Women

Employee rights for women in India aim to promote gender equality, safety, and fairness in the workplace. For instance, women employees in India are entitled to maternity leave and benefits under the Maternity Benefit Act.
They are also protected from sexual harassment at the workplace under the Sexual Harassment of Women at Workplace Act.
Additionally, women have the right to equal pay for equal work and a safe working environment free from discrimination and bullying.
Globally, women’s employee rights are protected by international conventions. The International Labour Organization’s (ILO) Equal Remuneration Convention ensures equal pay for equal work.
Women are also protected from discrimination, harassment, and bullying. The ILO’s Maternity Protection Convention provides for maternity leave and benefits.
Furthermore, women have access to affordable childcare and dependent care and are protected from gender-based violence and stalking.
These rights aim to create a fair and inclusive work environment where women can thrive and reach their full potential.
Employers must ensure compliance with these laws and promote gender equality in the workplace. Women employees must know their rights and speak up against any violations.
Lesser Known Employee Rights You Didn’t Know You Have!
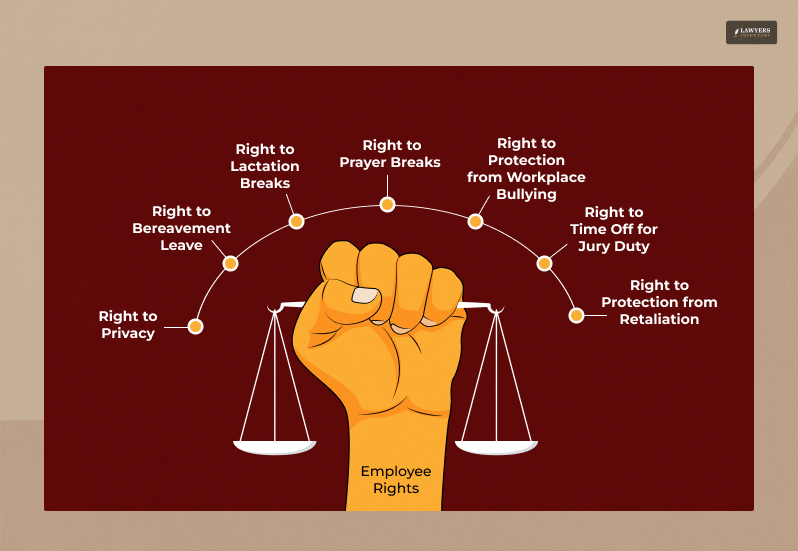
Now, coming to the most awaited part of the blog: are there rights you do not know about related to your work? Well, in most certainty, the answer is a big yes!
For instance, did you know you have the right to take breaks between your long work hours? Or the fact that you have the right to seek accommodation for disabilities? Yes, that is right.
Here is a list of the employee rights that you might not have any idea about, but you better know:
1. Right to Privacy
You have the right to privacy at work, like in your personal life. This means your employer can’t snoop on you by reading your personal emails or messages, listening to your phone calls, or searching your workspace or belongings without a valid reason.
Your employer must also respect your boundaries by keeping your personal information confidential and asking for your consent before sharing your data with others.
Additionally, they should provide a private space for sensitive conversations, such as discussions about your health or personal issues.
2. Right to Bereavement Leave
Losing a loved one can be a devastating experience, and that’s why you have the right to bereavement leave. This leave allows you to take time off work to attend funeral arrangements, grieve, and care for personal matters.
Typically, bereavement leave ranges from 3-5 days off for immediate family members, such as a spouse, child, or parent. For extended family members, like a grandparent or sibling, you may be entitled to 1-2 days off.
It’s essential to note that bereavement leave policies can vary depending on your company. Check your employee handbook or speak with HR to understand your specific provisions.
They can provide detailed information on your company’s bereavement leave policy so you can plan accordingly during a difficult time.
3. Right to Lactation Breaks
You have the right to lactation breaks at work if you are a breastfeeding mother. This permits you to take unpaid breaks to nurse your child or express milk whenever necessary.
Your employer must provide a quiet, uncluttered, secure, and distraction-free area for lactation breaks. Up to a year after giving birth, you can take breastfeeding breaks as frequently as necessary and for as long as needed.
For further information, see your company’s lactation break policy and inform your supervisor or HR about your needs. This guarantees nursing moms a cozy and encouraging setting to tend to their infants.
4. Right to Prayer Breaks
Yes, I bet you didn’t know about this!
It is your right to exercise your faith during prayer breaks at work. If possible, your employer must provide a secluded, peaceful area for prayer breaks. Spend a few minutes praying or meditating without worrying about criticism or consequences.
However, you must also remember that you should honor your work schedule and ensure that prayer breaks do not impede your responsibilities. Additionally, share your needs with your supervisor or HR, and for more information, go to your company’s policy.
Your employer is required to support your religious beliefs by providing reasonable accommodations. In this manner, work and faith can coexist together.
5. Right to Protection from Workplace Bullying
You have the right to work safely and respectfully without workplace bullying. This includes verbal, physical, or psychological abuse.
If you experience bullying, report it to your supervisor, HR, or a trusted colleague. Your employer must investigate and take prompt action to stop the bullying.
Workplace bullying is unacceptable and can lead to severe consequences for the bully. Don’t suffer in silence – seek help if you’re experiencing workplace bullying.
6. Right to Time Off for Jury Duty
You have the right to take time off work for jury duty. When you receive a jury duty summons, inform your employer and provide proof of the summons.
Your employer’s policy will determine whether you receive paid or unpaid leave during jury duty. Check your company’s policy to understand your entitlements.
Remember, your employer cannot penalize or discriminate against you for serving on a jury. Jury duty is a civic duty, and your employer must accommodate your absence.
Employees in many countries, including the US, Canada, and Australia, have the right to take time off for jury duty without penalty or discrimination.
However, this right does not exist in some countries like China, Japan, and India, where jury systems are limited or non-existent.
Employers in countries with jury systems must accommodate employees’ jury duty, ensuring they can fulfill their civic duty without work-related consequences.
7. Right to Protection from Retaliation
The next right that many people do not know about is the legal right of every employee to protect themselves from their employer’s retaliation.
You can speak up against workplace wrongdoing without fear of punishment in countries like the US, Canada, and Australia.
Retaliation, such as demotion, pay cuts, or firing, is illegal. If you report harassment, discrimination, or safety issues, you are protected from retaliation. If you experience retaliation, report it to HR, a supervisor, or a government agency.
You can also seek support from a union or legal aid organization. Remember, speaking up is a protected right, so don’t hesitate to report incidents and seek help if needed. This protection varies in countries like China and India.
Wrapping it Up!
Rights are nothing less that the basic necessities that we need to survive. Unless we have these, we cannot thrive. Employee rights are nothing less than other fundamental rights that we have as citizens of a country.
These rights allow us to work in organizations and feel protected and heard. While it is true that employee rights can differ from one country to another, it is best that you are aware of yours.
In case you want to know about employee rights, I hope that this blog has been of help to you. If there are any other questions related to the same, please let me know. Comment below in the box, and I will answer them all for you!
Read Also:
- Tips To Secure Your Employment Rights With The Best Lawyer?
- 5 Qualities To Look For When Hiring An Employment Lawyer
- 7 Things You Need to Know About Workers’ Compensation











0 Reply
No comments yet.